Best Orthopedic Surgeons in Artemis Hospital Gurgaon
 17 December,2025
Read More
17 December,2025
Read More
Enquire now in case of any assistance needed
 27 September,2024
27 September,2024

Lung transplants are common procedures nowadays. They are performed when a person's lungs become damaged or can not function properly. Some of the common diseases that require a lung transplant are cystic fibrosis, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), pulmonary fibrosis, or pulmonary hypertension.
Around 5,000 lung transplants are performed each year globally, and India is one of the top 20 preferred destinations where the most are performed annually.
Fill up the form and get assured assitance within 24 hrs!
A lung transplant is a surgical process in which diseased or damaged lungs are replaced with healthy lungs from a donor. This procedure is typically considered for individuals with severe, irreversible lung diseases that significantly impair their ability to breathe and live an everyday life.
A lung transplant is a procedure that is only carried out surgically when the lungs of an individual get damaged for a reason. The need for a lung transplant typically arises from severe, progressive lung diseases such as interstitial lung disease, bronchiectasis, lung cancer, congenital lung diseases, post-tuberculosis lung damage, and many more.
There are numerous types of lung transplants; some of the major types are as follows:
Lung transplants represent a significant improvement in medical science by replacing damaged lungs with healthy ones, offering a vital lifeline to those with serious lung diseases. The key benefits and improvements observed by patients who undergo lung transplants are:
Individuals who are suffering from severe lung disease and end-stage lung diseases are considered the right candidate for lung transplants if it contributes to the impairment of their quality of life. Also, it is an option for patients who are experiencing significant symptoms such as chronic cough, severe shortness of breath, and extreme fatigue, which significantly affects their daily activities.
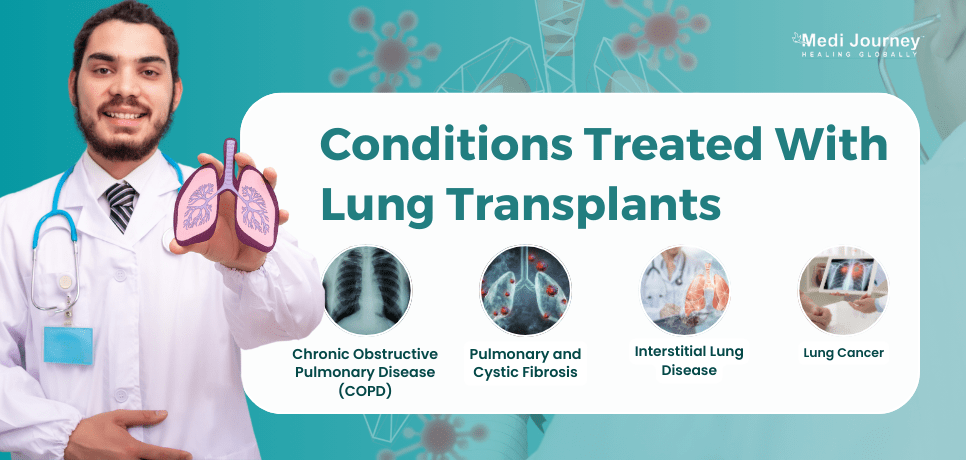
Lung transplants are often considered for patients with severe, life-threatening lung diseases when other treatments have failed to improve lung function. Some of the conditions treated with lung transplants are:
Understanding the lung transplant process is crucial for patients and their families, as it involves several stages, from evaluation to recovery. Below are the key aspects of what to expect during the lung transplant process:
The lung transplant surgery involves several key steps to ensure the successful replacement of damaged lungs with healthy donor organs.
Post-operative care following a lung transplant is critical to ensure a smooth recovery and long-term success. Some of the primary post-operative care steps after a lung transplant are as follows:
Recovery after a lung transplant includes several steps, such as:

The success rate and prognosis of lung transplants can depend on several factors, such as the recipient's overall health, the type of lung transplant conducted, and the quality of the donor's lungs.
Although there have been enormous advancements in the medical industry, a complex procedure like a lung transplant comes with its risks and complications. Some of the major and potential surgical complications associated with this procedure are:
Donor eligibility for a lung transplant generally includes the following:
Lung transplantation is a vital option for individuals with severe, irreversible lung diseases, significantly improving their quality of life and extending survival. By replacing damaged lungs with healthy donor organs, patients can experience enhanced breathing capacity, increased physical activity, and better daily living.
While lung transplantation has many benefits, it is crucial for patients to fully understand the associated risks and engage in comprehensive care and lifestyle adjustments for optimal outcomes. With careful planning and ongoing medical support, lung transplantation can provide a renewed chance at life for those in need.
Fill up the form and get assured assitance within 24 hrs!
Doctor of Pharmacy
Dr. Deepanshu Siwach is a skilled clinical pharmacist with a Doctor of Pharmacy degree.?He has 4+?years of experience and has worked with thousands of patients. He has been associated with some of the top hospitals, such as Artemis Gurgaon.
Dr. Sandeep Nayar is a prominent Pulmonologist with an experience of more than 33 years. His expertise lies in treatment of various respiratory conditions such as Interstitial Lung Disease, Diseases of the Chest, and Sleep Apnea....
Senior Consultant
Medical Oncologist
Nanavati Super Specialty Hospital, Mumbai
WhatsApp UsSenior Director
Gynecologist and Obstetrician, IVF Specialist
Max Super Speciality Hospital, Shalimar Bagh, New Delhi
WhatsApp UsSenior Director
Gynecologist and Obstetrician, IVF Specialist
Max Smart Super Speciality Hospital, Saket, New Delhi
WhatsApp UsSenior Director
Gynecologist and Obstetrician
Max Smart Super Speciality Hospital, Saket, New Delhi
WhatsApp UsSenior Director
Gynecologist and Obstetrician
Max Smart Super Speciality Hospital, Saket, New Delhi
WhatsApp UsSenior Director
Gynecologist and Obstetrician
Max Smart Super Speciality Hospital, Saket, New Delhi
WhatsApp UsThe Art of Effective Communication
 17 December,2025
Read More
17 December,2025
Read More
 16 December,2025
Read More
16 December,2025
Read More
 10 December,2025
Read More
10 December,2025
Read More
 09 December,2025
Read More
09 December,2025
Read More
 05 December,2025
Read More
05 December,2025
Read More
 04 December,2025
Read More
04 December,2025
Read More
Trusted by Patients
"I am Asim from Bangladesh and was looking for treatment in India for neuro. I visited many websites to get the complete information regarding the treatment but I was not satisfied as I was getting confused. In the meanwhile, one of my friends suggested I seek help from Medi Journey as he experienced his medical journey very smoothly and was satisfied with it. They have filtered the top 10 doctors as per experience, the success rate of surgery & profile, so it helps us to choose the best treatment in India. "
"For my knee surgery, Medi Journey guided me to BLK Hospital where I received exceptional care. The team's support and the expertise at BLK Hospital exceeded my expectations. Thank you Medi Journey for making my medical journey stress-free. "
"I came from Iraq for my granddaughter's eye surgery in India facilitated by Medi Journey, due to critical cases they advised us to get a second opinion from the different hospitals before going to surgery. Finally, we went to Fortis Escort Hospital, which helped us to get more confidence for diagnosis. Fortis Escort Hospital has the best eye surgeon team with the latest instruments. Thanks to all team members for providing a high-quality treatment in India at an affordable cost. "
"I came for my hair transplant in India, before coming I was so confused about choosing the best clinic and surgeon for me. But thanks to God one of my friends had a hair transplant in India through Medi Journey. He recommended me to go with them. I am completely happy with my experience with them. They were always very fast in their responses to me. the success rate of my hair transplant surgery is 100%."
"Artemis Hospital, suggested by Medi Journey, turned out to be a great choice for my treatment. The personalized assistance and medical care were exceptional. I'm grateful to Medi Journey for guiding me to a hospital that perfectly matched my needs. Highly recommended! "
"I came from Afghanistan for my treatment in India at Jaypee Hospital, Noida. I had a fantastic experience with Medi Journey. Kudos to them for their incredible support during my medical journey. They not only took care of all the logistics but also connected me with a fantastic healthcare team. Efficient, caring, and highly recommended for a hassle-free medical tourism experience."
"I am Adam from Kano, Nigeria, one of my friends from Nigeria was facilitated by Medi Journey, and he recommended us to go with them. I sent my all reports to them and within 48 hours they reverted with 4 options from different hospitals. They helped me to get a Visa letter from the hospital, arrange pick-up from the airport, and book a hotel for me. Their team is very honest and throughout our stay in India they are with us they are caring for us like his family members. BLK Hospital is the best hospital in India with a top surgical oncologist surgeon team, a very advanced OT, and a Radiotherapy department. I wish more success to Medi Journey. "
"Great experience at the Max Hospital for my spine surgery and was successfully done. I thank my neurosurgeon and his entire team. I recommended all of my country's people to Medi Journey for treatment in India, they choose the best hospital, the best doctors, and the best cost for patients."
"I came to India from Dhaka, Bangladesh for my father-in-law's cardiac surgery at Fortis Hospital. I was confused about choosing the best surgeon for him before coming, but their team helped me to choose the best hospital and best cardiac surgeon in India with very good cost and 100% success rate of surgery. I am very happy with the services, really they make my journey so comfortable that make me feel at home. Thanks again and I like people to choose "Medi Journey" as your travel guide. "
"I am Mohammad from Bangladesh came to India for my general health checkup. Medi Journey offers me the complete package including Pick-up from the airport, hotel services, and 24-hour assistance. They guide you to choose the best hospital in India, the best cost of treatment with top-most doctors and give you complete information about hotel booking, and pick-up from the airport before coming to India They have the best team to help. Always choose Medi Journey for your treatment in India."





