The Role of Government Initiatives in Promoting Medical Tourism in India
 02 April,2025
Read More
02 April,2025
Read More
Enquire now in case of any assistance needed
 23 September,2024
23 September,2024
The cranium or skull protects the brain and surrounding structures, including blood vessels, tissues, and the scalp. However, all these structures are susceptible to injury. Such injuries are collectively grouped under head injuries or acquired brain injuries. Acquired brain injuries can be of two types - traumatic or non-traumatic.
A traumatic brain injury happens due to external force to the head that causes some damage to the brain. They are one of the most prevalent causes of death or disability worldwide. As per the World Health Organization (WHO), around 69 million people encounter some form of traumatic brain injury annually. As a result, traumatic brain injuries are considered to be a “silent epidemic.”
Any traumatic brain injury can prove to be life-threatening and requires immediate medical attention. The effects of these injuries can last for a short period or lifelong. Most traumatic brain injuries are treatable, but it is possible to prevent them from occurring in the first place.
This blog explains traumatic brain injury, its types, signs and symptoms, treatment options, and prevention in detail.
A head injury that damages the brain, often as a result of an external physical force, is termed a traumatic brain injury (TBI). The damage can be caused by a sudden bump or jolt to the head or a foreign object penetrating the skull. In the case of skull fractures, the skull fragments themselves may penetrate the brain and cause injury. Based on the severity of the injury, it can cause temporary loss of function, permanent disability, coma, or even death.
Traumatic brain injuries are of several types depending on the cause, severity, features, and other factors. Most traumatic brain injuries are classified into two broad groups -
The Glasgow Coma Scale (GCS) helps determine the severity of a traumatic brain injury by scoring the patient’s reactions to stimuli on a scale of 3 to 15. Post-traumatic amnesia (PTA) duration and loss of consciousness (LOC) are also helpful in judging the severity. Depending on the severity, traumatic brain injuries are classified as -
Based on the area of the injury, traumatic brain injuries are of two types -
In several cases, focal and diffuse TBIs may be present at the same time as a result of the same traumatic event.
Post a traumatic brain injury, the time taken for brain damage to occur leads to two types of injuries -
Apart from primary, secondary, mild, moderate, and severe traumatic brain injuries, there are several other types too. These are -
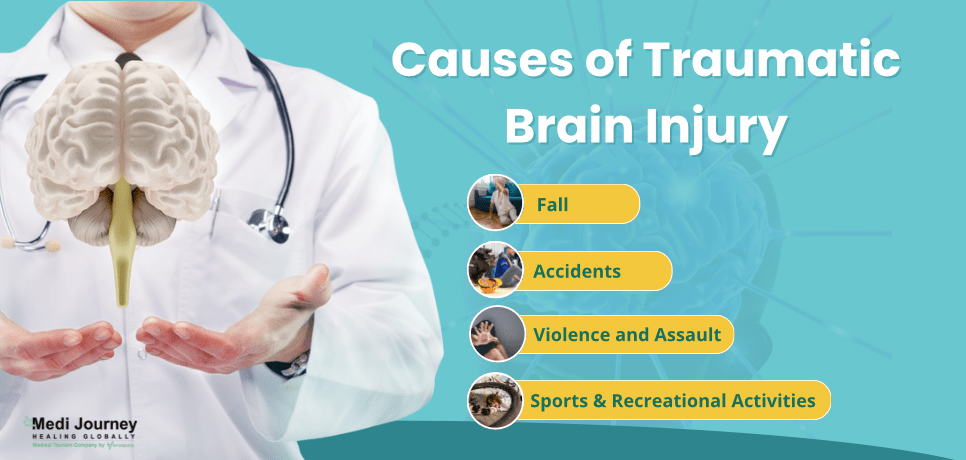
Traumatic brain injuries have several causative factors, including -
Symptoms of traumatic brain injury vary according to the severity of the injury. However, mild, moderate, and severe TBIs cause physical, cognitive, behavioral, and sensory alterations that manifest as symptoms of the injury.
When children experience a traumatic brain injury, they might not be able to express the symptoms they are dealing with. To determine a TBI in children, adults can look for symptoms such as -
If a traumatic head injury is suspected, the doctor will advise some diagnostic tests to confirm the injury and judge its extent. They will also attempt to determine the injury’s circumstances and causative factors. Tests used to detect a traumatic brain injury include -
The severity of a traumatic brain injury dictates its treatment. The doctor will administer the appropriate treatment once the injury is diagnosed and classified correctly.
Moderate or severe traumatic brain injuries are deemed medical emergencies. In this case, the doctor will ensure that the patient receives oxygen and blood supply and stabilize the patient to prevent further injuries.
In most cases, patients will require emergency surgery for various purposes. A surgeon will perform surgery to -
The doctor will prescribe certain medications for symptomatic relief from a traumatic brain injury and to minimize secondary damage to the brain. Some medicines used in the treatment of TBIs are -
A traumatic brain injury can lead to several complications, both short-term and long-term. These complications depend on the severity of the injury.
More severe forms of traumatic brain injuries have adverse effects on consciousness, physical complications, cognitive abilities, sensory functions, and emotional well-being.
The patient may experience varying levels of consciousness after a traumatic brain injury, such as -
TBIs cause impairment of cognitive abilities and communication problems, including-
Sensory complications of TBIs include -
Physical complications of TBIs include infections, seizures, hydrocephalus, hematomas, and vertigo.
Emotional and behavioral changes as a result of TBIs are depression, anxiety, mood swings, irritability, apathy, impulsiveness, insomnia, and drug or alcohol abuse.
TBIs also increase a person’s risk of degenerative brain diseases, such as Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s syndrome, and dementia pugilistica.
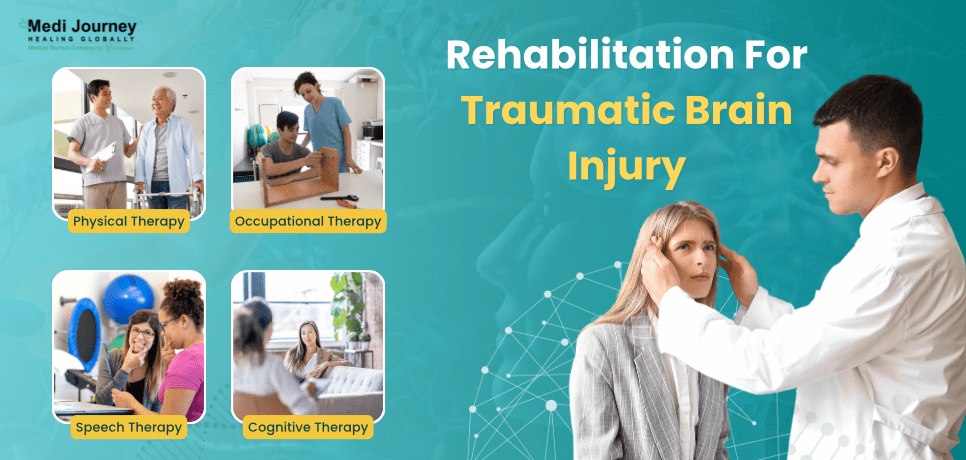
Patients with extensive traumatic brain injuries require rehabilitation to resume regular activities after the completion of treatment. Rehabilitation may include -
The prognosis of a mild to severe traumatic brain injury depends on multiple factors, such as the type of the injury, the area of the brain affected, access to emergency treatment, the patient’s age and overall health, and existing comorbidities.
In most cases, traumatic brain injuries are entirely preventable by taking some precautionary measures, such as -
The risk of falling, especially for older adults, can be minimized by -
TBIs in children are also preventable by taking steps such as -
A traumatic brain injury happens when there is a blow to the head, leading to brain damage. They are one of the most common causes of death and disability. Although traumatic brain injuries can have catastrophic consequences and lead to complications such as coma or death, they are almost always preventable by adopting some safety measures. TBIs of all severities must be treated as medical emergencies. If someone is experiencing signs of a traumatic brain injury, they must seek medical help immediately to prevent further complications.
BDS, Fellowship, MSc
Dr. Ishita Shirvalkar is a dentist, forensic odontologist, and medical writer. She has over two years of clinical experience. She completed her education at reputed institutions such as VSPM Dental College and Research Center in Nagpur.
Head of Department (HOD)
Neurosurgeon
Dr. Anil is a highly experienced Neuro and Spine Surgeon. He has 29+ years of experience and has successfully performed over 10,000 neurosurgical procedures. His expertise lies in Percutaneous Discectomy, Nucleoplasty training, and Minimal Access Spine Su...
Senior Consultant
Medical Oncologist
Nanavati-Max Super Speciality Hospital, Mumbai
Book Appointment WhatsApp UsSenior Director
Gynecologist and Obstetrician, IVF Specialist
Max Super Speciality Hospital, Shalimar Bagh, New Delhi
Book Appointment WhatsApp UsSenior Director
Gynecologist and Obstetrician, IVF Specialist
Max Smart Super Speciality Hospital, Saket, New Delhi
Book Appointment WhatsApp UsSenior Director
Gynecologist and Obstetrician
Max Smart Super Speciality Hospital, Saket, New Delhi
Book Appointment WhatsApp UsSenior Director
Gynecologist and Obstetrician
Max Smart Super Speciality Hospital, Saket, New Delhi
Book Appointment WhatsApp UsSenior Director
Gynecologist and Obstetrician
Max Smart Super Speciality Hospital, Saket, New Delhi
Book Appointment WhatsApp UsFill up the form and get assured assitance within 24 hrs!
The Art of Effective Communication
 24 January,2025
Read More
24 January,2025
Read More
Trusted by Patients
"I am Asim from Bangladesh and was looking for treatment in India for neuro. I visited many websites to get the complete information regarding the treatment but I was not satisfied as I was getting confused. In the meanwhile, one of my friends suggested I seek help from Medi Journey as he experienced his medical journey very smoothly and was satisfied with it. They have filtered the top 10 doctors as per experience, the success rate of surgery & profile, so it helps us to choose the best treatment in India. "
"For my knee surgery, Medi Journey guided me to BLK Hospital where I received exceptional care. The team's support and the expertise at BLK Hospital exceeded my expectations. Thank you Medi Journey for making my medical journey stress-free. "
"I came from Iraq for my granddaughter's eye surgery in India facilitated by Medi Journey, due to critical cases they advised us to get a second opinion from the different hospitals before going to surgery. Finally, we went to Fortis Escort Hospital, which helped us to get more confidence for diagnosis. Fortis Escort Hospital has the best eye surgeon team with the latest instruments. Thanks to all team members for providing a high-quality treatment in India at an affordable cost. "
"I came for my hair transplant in India, before coming I was so confused about choosing the best clinic and surgeon for me. But thanks to God one of my friends had a hair transplant in India through Medi Journey. He recommended me to go with them. I am completely happy with my experience with them. They were always very fast in their responses to me. the success rate of my hair transplant surgery is 100%."
"Artemis Hospital, suggested by Medi Journey, turned out to be a great choice for my treatment. The personalized assistance and medical care were exceptional. I'm grateful to Medi Journey for guiding me to a hospital that perfectly matched my needs. Highly recommended! "
"I came from Afghanistan for my treatment in India at Jaypee Hospital, Noida. I had a fantastic experience with Medi Journey. Kudos to them for their incredible support during my medical journey. They not only took care of all the logistics but also connected me with a fantastic healthcare team. Efficient, caring, and highly recommended for a hassle-free medical tourism experience."
"I am Adam from Kano, Nigeria, one of my friends from Nigeria was facilitated by Medi Journey, and he recommended us to go with them. I sent my all reports to them and within 48 hours they reverted with 4 options from different hospitals. They helped me to get a Visa letter from the hospital, arrange pick-up from the airport, and book a hotel for me. Their team is very honest and throughout our stay in India they are with us they are caring for us like his family members. BLK Hospital is the best hospital in India with a top surgical oncologist surgeon team, a very advanced OT, and a Radiotherapy department. I wish more success to Medi Journey. "
"Great experience at the Max Hospital for my spine surgery and was successfully done. I thank my neurosurgeon and his entire team. I recommended all of my country's people to Medi Journey for treatment in India, they choose the best hospital, the best doctors, and the best cost for patients."
"I came to India from Dhaka, Bangladesh for my father-in-law's cardiac surgery at Fortis Hospital. I was confused about choosing the best surgeon for him before coming, but their team helped me to choose the best hospital and best cardiac surgeon in India with very good cost and 100% success rate of surgery. I am very happy with the services, really they make my journey so comfortable that make me feel at home. Thanks again and I like people to choose "Medi Journey" as your travel guide. "
"I am Mohammad from Bangladesh came to India for my general health checkup. Medi Journey offers me the complete package including Pick-up from the airport, hotel services, and 24-hour assistance. They guide you to choose the best hospital in India, the best cost of treatment with top-most doctors and give you complete information about hotel booking, and pick-up from the airport before coming to India They have the best team to help. Always choose Medi Journey for your treatment in India."





