Best Orthopedic Surgeons in Artemis Hospital Gurgaon
 17 December,2025
Read More
17 December,2025
Read More
Enquire now in case of any assistance needed
 04 March,2024
04 March,2024

Lung cancer is one of the most widely diagnosed cancers among women and men. In 2023 alone, over 2.3 million people developed lung cancer. Around 80% of the cases are linked to cigarette smoking, making it a significant risk factor for the disease.
Early diagnosis is the critical element for curing lung cancer. However, if you have been diagnosed in later stages, keep hope. With the advancements in medical sciences, various new therapies that can benefit you are now available. Targeted therapy and immunotherapy, such as CAR T-cell therapy, have shown promising results and are now used to treat lung cancer.
However, prevention is better than cure. Hence, this blog aims at spreading awareness and knowledge about this fatal disease. It will answer all your questions regarding lung cancer, its types, symptoms, diagnosis, risks, prevention, and treatment.
Fill up the form and get assured assitance within 24 hrs!
Lung cancer is a complex respiratory disease that develops when the cells in the organ start diving uncontrolled. When the normal functioning of cell division gets hampered due to mutations, the cells keep dividing, ultimately forming a mass or tumor. The two prominent types of lung cancer are –
Complications of lung cancer include chest pain, shortness of breath, coughing up blood, and fluid in the chest (pleural effusion).
Lung cancer screening is one of the best ways to diagnose cancer in an early stage. It is done mainly by using low-dose CT scans for people who have been chronic smokers or have other associated risks.
For diagnosing cancer, the oncologist will start by asking about symptoms you are experiencing, taking a past medical & family history, and performing a physical examination. The next step involves running tests like a blood test and chest X-ray. If the physician suspects lung cancer, they will further investigate for an accurate diagnosis. It will include –

Lung cancer is associated with various risk factors. While you can control the most common risk factors, others can't be changed, such as family history. Risk factors for cancer of the lungs are –
Lung cancer is responsible for approximately 18% of all cancer deaths. The primary reason for it being so fatal is the late diagnosis of the disease. No apparent differentiating symptoms are visible when lung cancer begins and is in its early stages. Therefore, it is advisable to have regular screening tests and check-ups if you are at risk for developing lung cancer.
Some of the notable signs of lung cancer are –
Apart from these, lung cancer can also depict symptoms like bone pain, unexpected weight loss, headaches, fatigue, weakness, etc.
No one can guarantee an immunity against lung cancer. However, you can significantly reduce the odds of developing lung cancer by following these preventive measures –
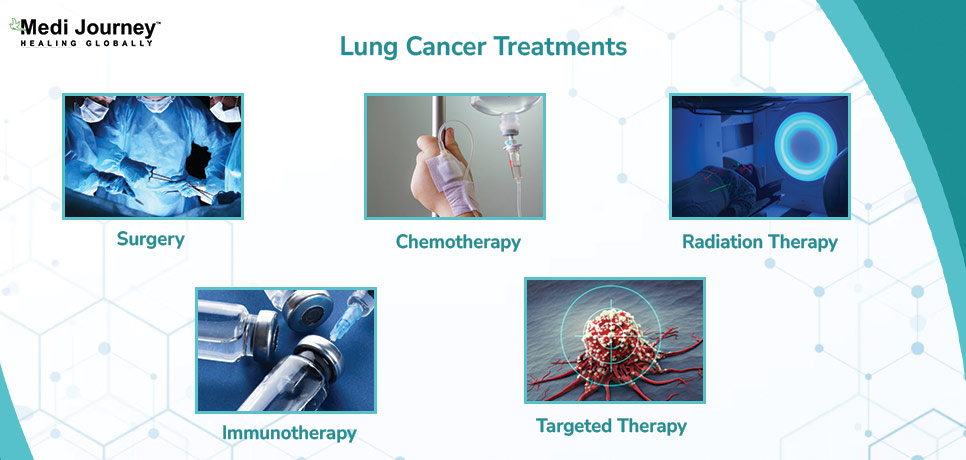
Your treating oncologist will make a tailored treatment plan based on your general health, possible side effects, type & stage of lung cancer, and your personal preference. The treatment plan is most likely to be a combination of –
Developing lung cancer is a daunting experience that not only affects you physically but also mentally. Getting timely diagnosis and treatment is crucial to battle the fatal disease. With the availability of personalized medicines and therapies, the lung cancer death rate has declined to some extent. Going for regular screening and following preventive measures is still considered the best way to win over lung cancer.
Fill up the form and get assured assitance within 24 hrs!
Doctor of Pharmacy
Dr. Deepanshu Siwach is a skilled clinical pharmacist with a Doctor of Pharmacy degree.?He has 4+?years of experience and has worked with thousands of patients. He has been associated with some of the top hospitals, such as Artemis Gurgaon.
Dr. Vivek Gupta is an experienced Surgical Oncologist with over 16 years of practice....
Senior Consultant
Medical Oncologist
Nanavati Super Specialty Hospital, Mumbai
WhatsApp UsSenior Director
Gynecologist and Obstetrician, IVF Specialist
Max Super Speciality Hospital, Shalimar Bagh, New Delhi
WhatsApp UsSenior Director
Gynecologist and Obstetrician, IVF Specialist
Max Smart Super Speciality Hospital, Saket, New Delhi
WhatsApp UsSenior Director
Gynecologist and Obstetrician
Max Smart Super Speciality Hospital, Saket, New Delhi
WhatsApp UsSenior Director
Gynecologist and Obstetrician
Max Smart Super Speciality Hospital, Saket, New Delhi
WhatsApp UsSenior Director
Gynecologist and Obstetrician
Max Smart Super Speciality Hospital, Saket, New Delhi
WhatsApp UsThe Art of Effective Communication
 17 December,2025
Read More
17 December,2025
Read More
 16 December,2025
Read More
16 December,2025
Read More
 10 December,2025
Read More
10 December,2025
Read More
 09 December,2025
Read More
09 December,2025
Read More
 05 December,2025
Read More
05 December,2025
Read More
 04 December,2025
Read More
04 December,2025
Read More
Trusted by Patients
"I am Asim from Bangladesh and was looking for treatment in India for neuro. I visited many websites to get the complete information regarding the treatment but I was not satisfied as I was getting confused. In the meanwhile, one of my friends suggested I seek help from Medi Journey as he experienced his medical journey very smoothly and was satisfied with it. They have filtered the top 10 doctors as per experience, the success rate of surgery & profile, so it helps us to choose the best treatment in India. "
"For my knee surgery, Medi Journey guided me to BLK Hospital where I received exceptional care. The team's support and the expertise at BLK Hospital exceeded my expectations. Thank you Medi Journey for making my medical journey stress-free. "
"I came from Iraq for my granddaughter's eye surgery in India facilitated by Medi Journey, due to critical cases they advised us to get a second opinion from the different hospitals before going to surgery. Finally, we went to Fortis Escort Hospital, which helped us to get more confidence for diagnosis. Fortis Escort Hospital has the best eye surgeon team with the latest instruments. Thanks to all team members for providing a high-quality treatment in India at an affordable cost. "
"I came for my hair transplant in India, before coming I was so confused about choosing the best clinic and surgeon for me. But thanks to God one of my friends had a hair transplant in India through Medi Journey. He recommended me to go with them. I am completely happy with my experience with them. They were always very fast in their responses to me. the success rate of my hair transplant surgery is 100%."
"Artemis Hospital, suggested by Medi Journey, turned out to be a great choice for my treatment. The personalized assistance and medical care were exceptional. I'm grateful to Medi Journey for guiding me to a hospital that perfectly matched my needs. Highly recommended! "
"I came from Afghanistan for my treatment in India at Jaypee Hospital, Noida. I had a fantastic experience with Medi Journey. Kudos to them for their incredible support during my medical journey. They not only took care of all the logistics but also connected me with a fantastic healthcare team. Efficient, caring, and highly recommended for a hassle-free medical tourism experience."
"I am Adam from Kano, Nigeria, one of my friends from Nigeria was facilitated by Medi Journey, and he recommended us to go with them. I sent my all reports to them and within 48 hours they reverted with 4 options from different hospitals. They helped me to get a Visa letter from the hospital, arrange pick-up from the airport, and book a hotel for me. Their team is very honest and throughout our stay in India they are with us they are caring for us like his family members. BLK Hospital is the best hospital in India with a top surgical oncologist surgeon team, a very advanced OT, and a Radiotherapy department. I wish more success to Medi Journey. "
"Great experience at the Max Hospital for my spine surgery and was successfully done. I thank my neurosurgeon and his entire team. I recommended all of my country's people to Medi Journey for treatment in India, they choose the best hospital, the best doctors, and the best cost for patients."
"I came to India from Dhaka, Bangladesh for my father-in-law's cardiac surgery at Fortis Hospital. I was confused about choosing the best surgeon for him before coming, but their team helped me to choose the best hospital and best cardiac surgeon in India with very good cost and 100% success rate of surgery. I am very happy with the services, really they make my journey so comfortable that make me feel at home. Thanks again and I like people to choose "Medi Journey" as your travel guide. "
"I am Mohammad from Bangladesh came to India for my general health checkup. Medi Journey offers me the complete package including Pick-up from the airport, hotel services, and 24-hour assistance. They guide you to choose the best hospital in India, the best cost of treatment with top-most doctors and give you complete information about hotel booking, and pick-up from the airport before coming to India They have the best team to help. Always choose Medi Journey for your treatment in India."





